

What options exist for corrosion control of nuts, bolts and washers?
There are several different methods whereby a zinc coating can be applied to fasteners to provide a protective coating. These include zinc or cadmium electro deposition (electroplating), mechanical plating, sherradizing, and hot dip galvanizing. All these processes provide a degree of protection. For practical reasons, the most commonly used systems are hot dip galvanizing and zinc or cadmium electroplating which is frequently and misleadingly described as electro galvanizing.
The two most important factors to consider when selecting the most effective protective system are resistance to mechanical damage of the protective coating during assembly and tensioning and the long-term protective properties of the coating. Let us consider these two important attributes and the degree to which they apply to both zinc electroplating and hot dip galvanizing. Incidentally, cadmium electroplating is frowned upon by environmentalists and in fact it is banned in many countries due to the toxic properties of this metal, particularly when the coating is cut or welded.
The resistance to mechanical damage and adhesion properties of both electroplating and hot dip galvanizing are far superior to those provided by organic coatings although the mechanism whereby adhesion is achieved is somewhat different in each case.
Hot dip galvanizing has the added benefit of a series of hard iron/zinc alloys within the coating structure. This significantly reduces the possibility of coating damage during tensioning.
As far as corrosion resistant durability is concerned, the thickness of a zinc coating determines its corrosion resistant life. Unfortunately, the thickness of a zinc coating that can be applied by the electro-deposition process is distinctly limited to the extent that the zinc electroplated coating applied to bolts and nuts is unlikely to exceed a thickness of about 10µm. In contrast, the coating applied by hot dip galvanizing normally averages between 50 and 60 µm in thickness which equates to at least five times the corrosion resistant life of a relatively thick zinc electroplated coating. In other words, hot dip galvanizing provides heavy-duty corrosion protection for fastener assemblies.
Heavy-duty coatings as in an additional 25% thickness that may be specified for structural steel cannot be achieved in the case of hot dip galvanized fasteners. The reason for this is that after the galvanizing process, all bolts and nuts must be efficiently centrifuged to remove excess zinc and if this were not done successfully, the oversized nut would not be able to freely screw onto the bolt.
The influence of silicon and or phosphorus content on hot dip galvanized coatings of steels is an interesting phenomenon.
The coating is therefore limited to about 60µm, which when viewed from a corrosion perspective, can be less protective when used to couple hot dip galvanized structural steel together. Structural steel normally results in a coating thickness of greater than 85µm and in the case of aggressive environments, when a heavy duty coating is specified, at least 105µm. To ensure that the corrosion resistant life of the hot dip galvanized fastener roughly equates to the life of the coating on the structure, additional protection in the form of a suitable paint may be used.
Most paints will adhere to well degreased galvanized surfaces but alkyd enamel paints should not be applied directly onto zinc.
A hot dip galvanized coating can be applied to bolts from M8 and upwards. Internal nut threads are tapped oversize to predetermined limits in order to accommodate the coating thickness provided by hot dip galvanizing. This does not have a negative effect on the mechanical properties of tensioned fasteners. Internal nut threads are not coated as this would necessitate oversize tapping to an extent that the strength of a fastener assembly could be compromised if tensioned to provide the specified clamping force as laid down in relevant specifications. The absence of a zinc coating on internal nut threads does not impact negatively on the corrosion resistant properties of hot dip galvanized fasteners due to the sacrificial properties of the surrounding zinc coating.
High strength bolts and nuts up to class 10.9 are now hot dip galvanized on a regular basis.

To position the Hot Dip Galvanizers Association of Southern Africa, comprising all its Members and other interested parties, as a professional organization serving the interests of all parties dependent upon the hot dip galvanizing industry. To develop and expand the demand for hot dip galvanizing, identify and develop new market opportunities for the benefit of Members and other Stakeholders.
Case Study: #27 2015
The performance of Pandrol rail fasteners in a marine environment on the Natal South Coast
Case Study: #26 2014
Case Study: #25 2014
Case Study: #24 2013
Case Study: # 23 2013
Volume 12, Issue 2: September 2015 (61)
Volume 12, Issue 1: May 2015 (60)
Volume 11, Issue 3: November 2014 (59)
Volume 11, Issue 2: November 2014 (58)
Volume 11, Issue 1: November 2014 (57)
Volume 10, Issue 4: November 2013 (56)
Volume 13, Issue 1: April 2016 (62)

1. APPEARANCE OF SODIUM DICHROMATE
What is this?
A small amount of Sodium Dichromate is generally added to the quench water bath for passivation.
Cause
Although the recommended quantity of Sodium Dichromate is about 0.15 to 0.3%, occasionally when topping up, more is added. This often results in a dark yellow to brown colour on the galvanized surface. The darker colour will provide enhanced initial corrosion protection.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted since there is no adverse effect on corrosion control.
The galvanizer should maintain the concentration of Sodium Dichromate at about 0.15 to 0.3%.
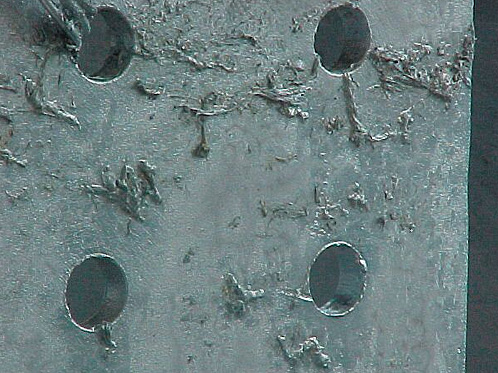
2. ASH DEPOSITS
What is this?
Ash deposits are grey, non-metallic deposits consisting of zinc oxide that have been deposited on the hot dip galvanized coating.
Cause
Zinc oxide deposits can take place when the component is dipped or when it is removed from the bath.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted or negotiated dependent on functional requirements since the coating is normally intact underneath the ash deposits. If required, ash must be removed by the galvanizer and the coating thickness verified for conformance to the specification requirements. In the case of liquid conveyance pipes, all ash should be removed.

3. BARE SPOTS
What is this?
Although excluded from SANS 121:2011 (ISO 1461:2009), bare spots of about 5mm2 (2.2 x 2.2mm), due to small localised flaws, are adequately protected by the sacrificial properties of zinc and will have very little effect on the service life of the coating.
Cause
There are several causes of bare spots. These include:
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Where necessary, such spots may be repaired using one of the specified repair methods. Gross uncoated areas are a cause for rejection.
The galvanizer should avoid overdrying and maintain the correct level of aluminium content in the kettle.

4. BLASTING DAMAGE
What is this?
Sweep blasting (done correctly) substantially increases paint adhesion and final coating appearance. However, done incorrectly it can result in coating damage.
Cause
Incorrect nozzle pressure; nozzle angle; sweeping distance; size of abrasive and recycling of grit.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This is cause for rejection as a hot dip galvanized coating will be partially or fully destroyed by excessive blasting. Refer to the HDGASA Code of Practice.

5. BLOWOUTS
What is this?
Staining and coating defects around unsealed weld areas and vent holes. Similar to stains caused by weeping. See Surface Condition 26
Cause
Pre-treatment chemicals penetrating sealed overlap areas through the required vent holes and escaping during immersion in the molten zinc. This effect tends to damage the flux coatings, causing localised uncoated areas.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted once repaired after cleaning.
The Designer and fabricator should take this into account during the design and manufacturing phase of the project.

6. CLOGGED HOLES
What is this?
Zinc film clogging or partly bridging holes.
Cause
Molten zinc has a high surface tension and will not easily drain from holes under 8mm in diameter.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted once the item has been cleaned if required.
The Designer should make the holes as large as possible.
The removal of molten zinc over the bath by the galvanizer will reduce the likelihood of clogging.
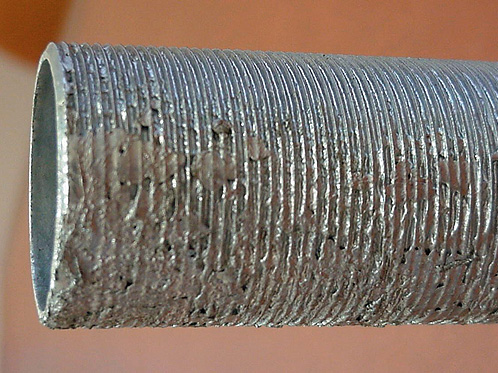
7. CLOGGED THREADS
What is this?
Threaded components or attachments have threads clogged with zinc.
Cause
Insufficient centrifuging or poor drainage of threaded attachments on withdrawal from the galvanizing bath.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This should be rejected and then cleaned by the galvanizer. The correct centrifuging equipment or post galvanizing thread cleaning by heating and wire brushing or oversize tapping of nuts, will generally remove clogging.
If necessary, specify delivery of bolts and nuts in nutted up form.

8. DAMAGED COATINGS CAUSED BY WELDING OR NON-CONVENTIONAL FIXING METHODS DURING ERECTION
Cause
Conventional drilling and bolting after hot dip galvanizing is preferred. Should welding or a non-conventional method of fixing be used, which results in damage to the coating, an approved repair method is necessary.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Coating repair can be done by zinc metal spraying or a zinc rich paint or epoxy, providing the product conforms to the requirements of the specification.
9. DISCOLOURATION AFTER HOT DIP GALVANIZING CAUSED BY GRINDING OR OTHER RESIDUES
Cause
Material stored in contact with rusty steel or iron filings, can cause surface rust staining.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted as once the cause has been removed the stains will gradually disappear. The Fabricator should clean if possible.
10. DISTORTION
What is this?
Distortion is the unwanted warping that occasionally becomes evident after hot dip galvanizing.
Cause
The hot dip galvanizing process occurs at a molten zinc temperature of 450°C. This is at the lower end of the stress relieving temperature for treating steel. Thus, any inherent rolling or welding stresses in the fabrication are likely to be released. This may result in a dimensional change, i.e. distortion.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The Designer has the following options available: use symmetrical designs; use sections of similar thickness; stiffen unsupported thin wall sections; use preformed members with the correct minimum bend radii; use balanced or staggered welding techniques; make use of temporary braces on thin walled sections such as troughs, cylinders and angle frames.
Stress Relief assembly prior to hot dip galvanizing.
The galvanizer should avoid quenching after galvanizing.
The components can be straightened after hot dip galvanizing.
11. DRAINAGE SPIKES
What is this?
Spikes and teardrops of zinc often appear along the edge of a component after hot dip galvanizing.
Cause
The edge most likely to have these spikes is the last to leave the bath on withdrawal. This applies particularly to complex fabrications.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Drainage spikes are easily removed at the bath while still molten but any solidified spikes should be removed by careful fettling by the galvanizer prior to release.
12. DULL GREY OR MOTTLED COATING APPEARANCE
What is this?
Dull grey or mottled coatings can appear as a dark grey circular pattern, a localised dull path, or may extend over the entire surface of the component.
Cause
This appearance indicates the presence of extensive iron / zinc alloy phase growth, caused by steels with high reactive levels of Silicon and Phosphorus.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Although not as aesthetically pleasing, a dull grey coating provides similar or better corrosion protection.
What is this?
Ash which has not been removed from the surface of the molten zinc prior to immersion of steel can be trapped on the steel surface as it is immersed and result in an uncoated surface beneath the trapped ash.
Cause
Inadequate skimming of ash from the molten zinc surface prior to dipping.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
On removal of entrapped ash, small uncoated surfaces shall be repaired according to the requirements of SANS 121: 2011 (ISO 1461:2009) by the Galvanizer.
Large defects greater than 0.5% of total surface area or single spots over 10cm2 are a cause for rejection and require stripping and re-galvanizing.
 14. FLAKING OR DELAMINATION OF COATING
14. FLAKING OR DELAMINATION OF COATING
What is this?
No adhesion of zinc to the steel surface or a thick, rough coating.
Cause
High phosphorus content greater than 0.02% can cause the entire coating to delaminate from the steel.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The Designer should use a steel that has a phosphorus content of lower than 0.02%.
 15. FLUX DEPOSITS, STAINS AND INCLUSIONS
15. FLUX DEPOSITS, STAINS AND INCLUSIONS
What is this?
Flux deposits or stains from the galvanizing process may adhere to the steel or become included in the coating. Flux residues are black, brown, grey or yellowish non-metallic deposits consisting mainly of ammonium chloride.
Cause
Flux deposits or stains may occur as a result of excessive (dusting) with ammonium chloride on withdrawal from the molten zinc. Flux inclusions can occur when a surface flux blanket is applied to the zinc surface (wet galvanizing). Flux blankets are normally only used for specialised processes, e.g. galvanizing tubes and fasteners.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Flux deposits or stains should be removed by the galvanizer and the underlying coating measured to determine whether it conforms to the minimum requirements of the specification.
 16. DISCOLOURATION OF THE PAINT COATING OVER HOT DIP GALVANIZING AFTER EXPOSURE TO THE ENVIRONMENT
16. DISCOLOURATION OF THE PAINT COATING OVER HOT DIP GALVANIZING AFTER EXPOSURE TO THE ENVIRONMENT
Cause
Inadequate repair of a damaged surface on the hot dip galvanized coating prior to the application of a paint coating.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
It is the installers responsibility to ensure the correct repair materials and application procedures are used when touching up cut or welded hot dip galvanized components and prior to painting. Where corrosion control has been compromised the job should be rejected.
What is this?
Mechanical handling or transport damage can occur, particularly with extremely thick coatings.
Cause
The use of chains, wire ropes, dragging or dropping of the component onto a hard surface, can cause mechanical damage. This is particularly relevant with thick coatings.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted and repaired by the galvanizer or builder if necessary.
Warning labels highlighting possible damage if manhandled should be attached by the galvanizer before the component is transported. The use of nylon lifting slings is recommended.
What is this?
Light aluminium oxide film lines on a hot dip galvanized surface.
Cause
Due to the shape and / or drainage conditions of some components, the hoist crane has stopped and started upon withdrawal of the items from the molten zinc.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted as it has no effect on corrosion resistance, with the overall appearance becoming uniform in time.
What is this?
Pimples or blisters formed during hot dip galvanizing are usually associated with surface imperfections such as dross inclusions.
Cause
Dross pimples result from agitation of the dross layer at the bottom of the bath or from dragging material through the dross layer. They appear as small, hard lumps on an otherwise normal galvanized surface. Blisters may be formed by hydrogen, which is absorbed during pickling and diffused at galvanizing temperatures.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted since dross pimples represent minor disturbances in coating uniformity and do not affect corrosion resistance. Smooth if sufficiently sharp to create the risk of injury.
The galvanizer should avoid disturbing the dross layer at the bottom by controlling immersion depth and drossing regularly.
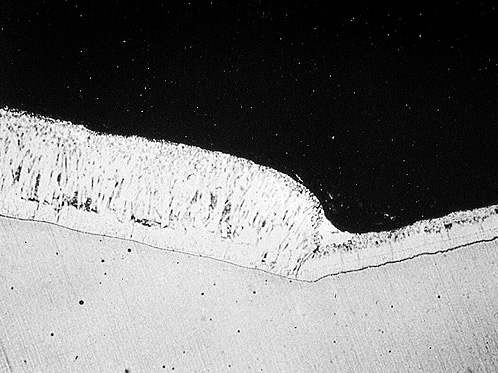 20. REACTIVE AND NON-REACTIVE STEELS, WELDED TOGETHER
20. REACTIVE AND NON-REACTIVE STEELS, WELDED TOGETHER
What is this?
Variations in coating thicknesses can arise when reactive and non-reactive steels are welded together. Efforts to increase coating thickness on the less reactive steel may result in an undesirably thick and brittle coating on the most reactive steel.
Cause
This difference in coating thickness is brought about by a combination of a more reactive silicon killed steel and / or high phosphorus, resulting in a thicker coating and a less reactive aluminium killed steel, resulting in a coating thickness sometimes below that required in the specification.
Should the galvanizer be asked to regalvanize in accordance with the specification, the resultant coating thickness on the reactive steel will be excessively thick, resulting in a brittle coating more susceptible to damage.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The fabricator should select the same steel for fabricating on a component.
If need be, accept a concession request by the galvanizer when the thinner coating is possibly below specification.
 21. REMOVAL OF ZINC COATING BY EXCESSIVE CLEANING
21. REMOVAL OF ZINC COATING BY EXCESSIVE CLEANING
What is this?
Unless otherwise agreed, the galvanizer will limit cleaning of the final coating by mechanical means to that required in the specification.
Cause
Excessive cleaning of the coating by mechanical methods can result in uncoated areas.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Care should be exercised by the galvanizer to avoid over cleaning. If corrosion control has been compromised, i.e. exposed areas greater than tolerance; reject.
Alternatively repair in accordance with standards.
What is this?
These defects may be broadly classified as surface discontinuities in the steel that have been elongated during rolling.
Cause
Steel may occasionally include laminations, laps, folds and non-metallic impurities, which result in slivers rolled into the metal surface. Defects of this type are sometimes detected before or after pickling, but may only become apparent after hot dip galvanizing.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted, as minor surface defects will not adversely influence coating life.
Surface flaws in the base material may be removed by local grinding after hot dip galvanizing followed by repair of the affected surface.
 23. ROUGH COATINGS, CAUSED BY STEEL SURFACE CONDITIONS
23. ROUGH COATINGS, CAUSED BY STEEL SURFACE CONDITIONS
Cause
Rough surfaces, typical of coatings on corroded steel surfaces, can be hot dip galvanized satisfactorily. The coating will however, reflect the texture of the substrate. Other causes of rough surfaces include uneven cold working, over pickling, a high galvanizing temperature and / or extended immersion in the molten zinc.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This can be accepted as the rougher surface will produce a thicker coating and result in a longer service life.
 24. ROUGH, HEAVY COATINGS CAUSED BY A ROUCH SURFACE AND / OR THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE STEEL – “TREE BARK EFFECT”
24. ROUGH, HEAVY COATINGS CAUSED BY A ROUCH SURFACE AND / OR THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE STEEL – “TREE BARK EFFECT”
Cause
Hot dip galvanized components showing markedly rough surfaces. This can include coatings that have a generally rough surface and, in some cases, groove type surface configurations, “tree bark effect” caused by variations in surface steel analysis.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The thicker coating produced will provide greater corrosion protection; except when the coating tends to flake off or delaminate (see surface condition 14).
 25. ROUGH HEAVY COATINGS CAUSED BY INSUFFICENT CENTRIFUGING
25. ROUGH HEAVY COATINGS CAUSED BY INSUFFICENT CENTRIFUGING
Cause
Efficient centrifuging will generally remove excess zinc and provide a smooth and attractive exterior.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Provided the steel / casting surface is reasonably smooth, correctly centrifuged articles will provide an acceptable finish.
Should the surface not be reasonably smooth; it should be rejected.
Cause
The salts from acid or flux that have penetrated porous welding or between contact surfaces during pickling, can weep after hot dip galvanizing and water quenching, providing a stained area.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Weld seepage stains are not a cause for rejection. The stains can be easily removed by means of bristle brushing. Should the component be destined for a corrosive area, the crevice may be sealed after cleaning.
 27. TIGHTHLY ADHERENT LUMPS OF ZINC ON THE INSIDE OF HEAVY WALLED STEEL PIPING
27. TIGHTHLY ADHERENT LUMPS OF ZINC ON THE INSIDE OF HEAVY WALLED STEEL PIPING
Cause
Heavy walls and thick flanges used in the manufacture of piping can act as a heat sink when immersed in molten zinc. This effect considerably lengthens the immersion time. Occasionally the galvanizer will remove the pipes before all the zinc has melted from the inside of the pipe.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The inspector should reject this. The galvanizer should ensure all zinc has been removed from the inside of the pipe by longer immersion times.
The item can be cleaned or repaired if acceptable to the customer.
What is this?
The zinc in the galvanizing bath should have free access to all component surfaces otherwise small uncoated or damaged areas can result.
Cause
Articles entering the galvanizing bath should not be in tight contact with each other. Jigging wire should also be loosely attached to eliminate wire marks. Where a component has been resting on jigging or dipping equipment, an uncoated area or touch mark could appear.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The galvanizer should minimise contact between components and jig connections (loosen jigging wire). Small components can be centrifuged.
These areas should be repaired if within allowable limits.
 29. TYPICAL SPANGLED HOT DIP GALVANIZED COATING
29. TYPICAL SPANGLED HOT DIP GALVANIZED COATING
What is this?
A typical hot dip galvanized surface is shown in the example. The surface is silver grey in colour and not necessarily, but often has, a spangled effect (zinc crystals) in a range of sizes.
Cause
Surface appearances may vary according to the chemical composition of the steel. Cooling rate has a direct effect on the surface brightness and spangle size. Faster cooling usually results in a brighter coating with a smaller spangle size.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Not rejectable if coating thickness within allowance limits.
What is this?
Uneven drainage results in an uneven or lumpy area on which zinc build up has occurred.
Cause
This can occur over the entire surface or in isolated areas. Uneven drainage also includes drips on the ends of parts, runs near holes. A cause may be high withdrawal speed and / or the galvanizing temperature being too low.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
This condition does not adversely affect coating performance and is acceptable.
However, protuberances and lumps which interfere with mating surfaces are unacceptable.
 32. UNGALVANIZED SURFACES CAUSED BY SCALE OR SAND
32. UNGALVANIZED SURFACES CAUSED BY SCALE OR SAND
Cause
Sand on cast iron or scale on the steel surface is generally caused by the process used to form or roll the product. A localised ungalvanized area in an otherwise continuous coating can occur if scale or sand from the moulding or rolling is not removed by acid pickling or abrasive blasting.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
These ungalvanized areas may occur in a linear pattern on angles, channels or other rolled products. They can also appear on cast iron products.
Uncoated areas within the limits of 0.5% of total area or single areas of 10cm2 or less can be repaired. Larger areas are rejectable.
 31. UNCOATED SURFACES CAUSED BY STEEL SURFACE CONTAMINANTS OR ENTRAPPED AIR
31. UNCOATED SURFACES CAUSED BY STEEL SURFACE CONTAMINANTS OR ENTRAPPED AIR
Cause
Residues (such as oil based paint, grease, oil or labels) on the steel surface or incorrectly positioned vent holes, can result in localised ungalvanized areas in an otherwise continuous galvanized coating. Uncoated areas often manifest themselves as black or very dark coloured spots.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
To avoid uncoated surfaces, ensure all paint or grease is removed prior to hot dip galvanizing. Make use of suitable marking pens for temporary identification. Correctly position adequately sized vent holes.
Uncoated areas within the limits of 0.5% of total area or single areas of 10cm2 or less can be repaired. Larger areas are rejectable.
 33. UNGALVANIZED AREA IN THE VICINITY OF A WELD
33. UNGALVANIZED AREA IN THE VICINITY OF A WELD
Cause
A localised ungalvanized area near a weld can be caused by weld slag deposit, weld porosity or weld undercut. residues from welding are resistant to normal pickling acids and must be removed before the work is pickled and hot dip galvanized.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Weld slag deposits should not be accepted prior to galvanizing and must be removed by the fabricator by means of abrasive blast cleaning. The deposit can also be removed by proper chipping or wire brushing.
Gas shielded welding(MIG/TIG) as opposed to stick welding is preferred for components which are to be hot dip galvanized.
Since corrosion control is compromised, this is rejectable; but may be repaired after negotiation.
What is this?
Weld spatter is oxidised, normally spherical expelled weld metal, that is fused (or not) onto the surrounding material during welding.
Cause
Weld spatter is caused by weld pool explosions when improper welding parameters are used, or if the material is dirty or contaminated.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Loosely adherent weld spatter should be removed by the fabricator prior to hot dip galvanizing. Although not acceptable in terms of the specification, the presence of tightly adherent weld spatter after hot dip galvanizing will not affect the corrosion resistant properties of the coating.
 35. WET STORAGE STAIN OR WHITE RUST
35. WET STORAGE STAIN OR WHITE RUST
What is this?
Wet storage stain or white rust (as it is commonly called) is a white voluminous deposit that is occasionally found on the surface of a freshly galvanized coating.
Cause
Wet storage stain (zinc hydroxide) is formed on freshly galvanized surfaces which are in close contact in the presence of moisture.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
Wet storage stain ceases when the cause is eliminated, i.e. the objects are separated and dried. Once it has been removed (with a nylon bristle brush) an evaluation is possible. If the coating thickness at the affected area is equal to, or greater than the minimum required in the specification, it is not a cause for rejection. The customer is to exercise caution during transport and storage to eliminate the susceptibility to wet storage stain.
 36. ZINC METAL SPRAYED REPAIR APPLIED TO INADEQUATELY BLASTED SURFACES OR NOT WIRE BRUSHED AFTER APPLICATION
36. ZINC METAL SPRAYED REPAIR APPLIED TO INADEQUATELY BLASTED SURFACES OR NOT WIRE BRUSHED AFTER APPLICATION
Cause
In order for zinc metal spraying to adhere on applications, the damaged galvanized surface must be adequately roughened by sweep blasting or other approved methods. As it is difficult not to overspray, excess zinc metal spray loosely adheres to the surrounding coating.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The fabricator or galvanizer must prepare the surface for repair by roughening the surface by sweep blasting or some other approved method. Loosely applied zinc metal sprayed coating at the perimeter of the repair should be removed by wire brushing. If not removed, there is no compromise in the corrosion resistance.
What is this?
Splashes and flakes of loosely adherent zinc, caused by moisture on the steel surface when hot dip galvanizing.
Cause
When hot dip galvanizing on unusually deep fabrications by double dipping, moisture on the surface of the steel contacts with the molten zinc causing splashes of zinc to loosely adhere to the already hot dip galvanized surface.
Effect / Remedy / Responsibility
The loosely adherent zinc splashes are easily removed and should be prior to release. An experienced galvanizer can ensure the coating overlap on double end dipped surface, is not visible.
Volume 10, Issue 3: August 2013 (55)
Volume 10, Issue 2: May 2013 (54)
Volume 10, Issue 1: February 2013 (53)
Volume 9, Issue 3: August 2012 (52)
Volume 9, Issue 2: June 2012 (51)
Volume 9, Issue 1: March 2012 (50)
Volume 8, Issue 4: November 2011 (49)
Volume 8, Issue 3: August 2011 (48)
Volume 8, Issue 2: June 2011 (47)
Volume 8, Issue 1: March 2011 (46)
Volume 7, Issue 4: November 2010 (45)
Volume 7, Issue 3: August 2010 (44)
Volume 7, Issue 2: June 2010 (43)
Volume 7, Issue 1: April 2010 (42)
Volume 6, Issue 4: November 2009 (41)
Volume 6, Issue 3: August 2009 (40)
Volume 6, Issue 2: June 2009 (39)
Volume 6, Issue 1: March 2009 (38)
Volume 5, Issue 4: November 2008 (37)
Volume 5, Issue 3: August 2008 (36)
Volume 5, Issue 2: June 2008 (35)
Volume 5, Issue 1: March 2008 (34)
Volume 4, Issue 4: November 2007 (33)
Volume 4, Issue 3: August 2007 (32)
Volume 4, Issue 2: June 2007 (31)
Volume 4, Issue 1: March 2007 (30)
Volume 3, Issue 4: November 2006 (29)
Volume 3, Issue 3: August 2006 (28)
Volume 3, Issue 2: June 2006 (27)
Volume 2, Issue 2: June 2005 (23)
Volume 2, Issue 1: March 2005 (22)
Volume 1, Issue 2: November 2004 (21)
Volume 1, Issue 1: August 2004 (20)
Volume 12, Issue 2: September 2015 (61)
Volume 12, Issue 2: September 2015 (61)
FOCUS ON: This issue looks at the industry from a few practical perspectives:
latest tagging technologies.
galvanizing corrosion control available to this key African industry.
using this technology for many decades to come.
to see the plate rolling mill and continuous sheet galvanizing facility, the event went well
and more may be arranged in the future.
Volume 12, Issue 2:
FOCUS ON: This issue looks at the industry from a few practical perspectives:
latest tagging technologies.
galvanizing corrosion control available to this key African industry.
using this technology for many decades to come.
to see the plate rolling mill and continuous sheet galvanizing facility, the event went well
and more may be arranged in the future.
Volume 12, Issue 2: September 2015 (61)
FISHBONE SURFACE PROFILE
(Condition: surface unevenness)
Fish-boning is an irregular pattern over the entire surface of the steel part, which is caused by differences in the surface chemistry of a large-diameter steel piece and variations in the reaction rate between the steel and molten zinc. It is caused by drainage around the pipe of the molten zinc, which is close to its freezing point at 419.5 °C, as it is extracted from the zinc bath. On withdrawal, the pipe is held at an angle to the zinc. As the pipe emerges, vertically raised, but still lying at an angle from horizontal, the zinc drains vertically. These ‘runs’ cool as they drain around the outer surface of the pipe, leaving a fishbone pattern. This surface condition does not affect the corrosion control performance of the hot-dip galvanized coating and is not rejectable.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |